Products
- Home
- Products
- Product/technological information
- Design and Characteristics of Bearings
Product/technological information
2. Design and Characteristics of Bearings
Bearing Structure

Boundary Dimensions
The boundary dimensions of bearings are the dimensions which indicate the external geometry of a bearing, including the bore diameter d, outside diameter D, width B or height T, and chamfer dimension r. These dimensions are required when mounting a bearing on a shaft or in housings.

d:Nominal bore diameter
D:Nominal outside diameter
B:Nominal bearing width
r:Chamfer dimensions of inner ring and outer ring (Minimum value)

d:Nominal bore diameter of shaft washer (inner ring)
d1:Nominal outside diameter of shaft washer (inner ring)
D:Nominal outside diameter of housing washer (outer ring)
D1:Nominal bore diameter of housing washer (outer ring)
T:Nominal height of bearing
r:Chamfer dimensions of shaft washer (inner ring) and housing washer (outer ring) (Minimum value)
Difference by Dimension Series of Bearing Cross-Section

The outside diameter and width dimension of the diameter series increase in order from 7 → 3 to the same bore diameter dimension.
Bearing Types

Standard

Extended inner ring
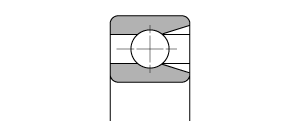
V:Full complement of balls

N:With a locating snap ring groove

NR:With a locating snap ring

F:With flange

N2:With double grooves

C1:With single chamfered edge for guides

C2:With double chamfered edge for guides

AV:With V-groove

LR:R outer surface

AU:With U-groove

A:Double-row angular

DB:Back-to-back duplex

DF:Face-to-face duplex

DT:Tandem duplex
Features of Bearings
| Load | Single-row deep groove ball bearings can support an axial load on both sides and moment loads in addition to a radial load. However, full complement ball bearings are for low speed radial loads, and can only support a slight axial load. |
|---|---|
| Rotational speed | The limiting speed differs by the bearing dimensions, manufacturing accuracy, type of cages, lubrication method, sealing method and load. |
| Torque and Noise | Single-row deep groove ball bearings manufactured with high accuracy demonstrate low torque and noise. |
| Inclination of outer ring / inner ring | Inclination occurs between the outer and inner rings of a bearing when there is poor accuracy of the shaft and housing, mounting errors and deflection of the shaft. However, the internal clearance of the bearing will allow such inclination to some extent. |
| Rigidity | When loads are imposed on a bearing, some elastic deformation occurs in the contact areas between the rolling elements and the raceways. The amount of elastic deformation changes according to the dimensions and type of bearing and the load applied to it, and bearings with larger dimensions demonstrate higher rigidity. |
| Mounting and Dismounting | Single-row deep groove ball bearings are a non-separable bearing therefore, it is necessary to design the shaft and housing in consideration of periodic inspections and replacement. |
| Positioning of axial direction | Bearings with flange and locating snap ring are more effective for positioning the axial direction. |
Classification by Bearing Dimensions
* Unit: mm
| Bearing Classification of Our Company | Nominal bore diameter | Nominal outer diameter |
|---|---|---|
| Extra-miniature bearing | d≦2 | D≦7 |
| Miniature bearing | d≦5 | D<9 |
| Small bearing | d<10 | D≧9 |
| Large bearing | d≧10 | D≧15 |
